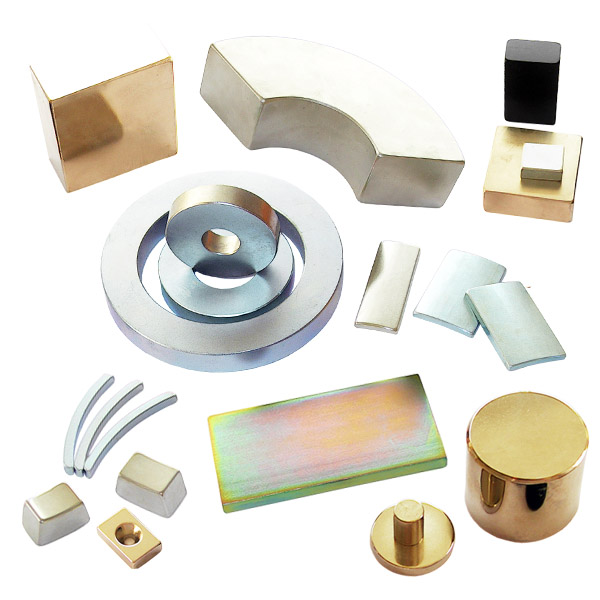
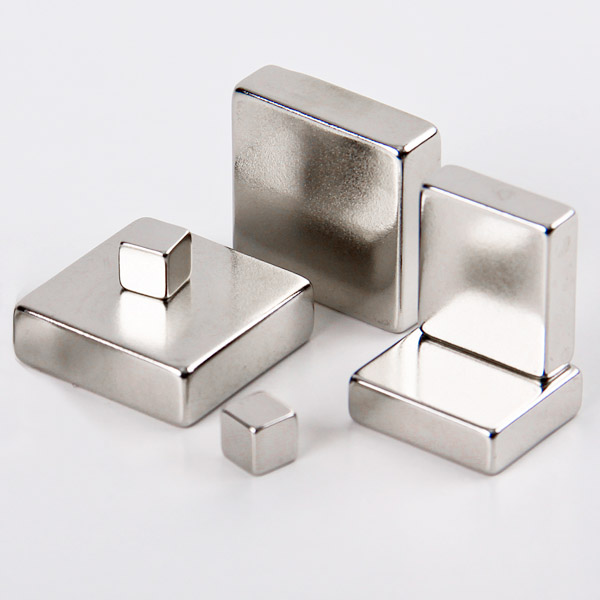
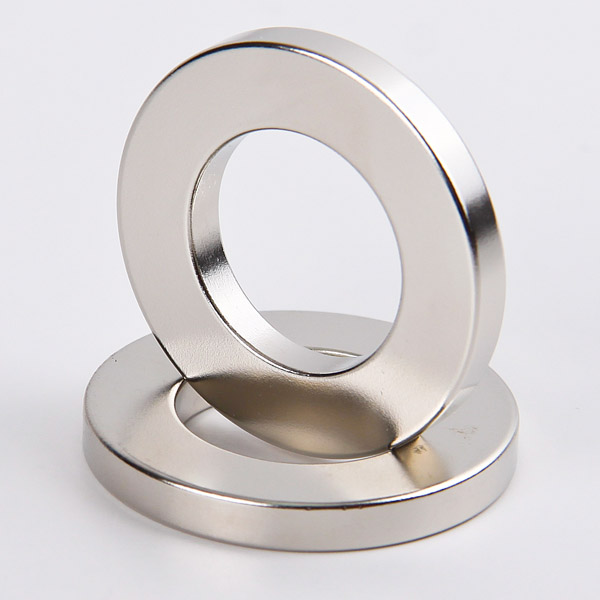
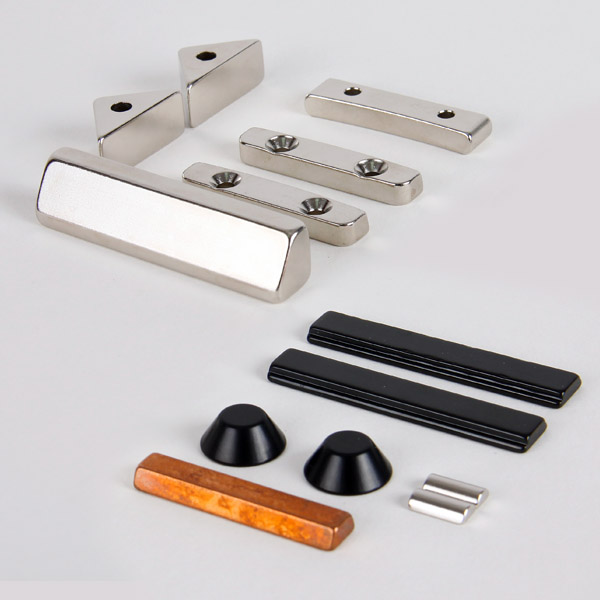
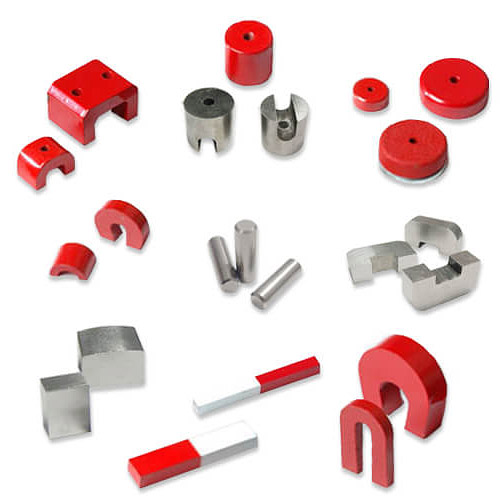
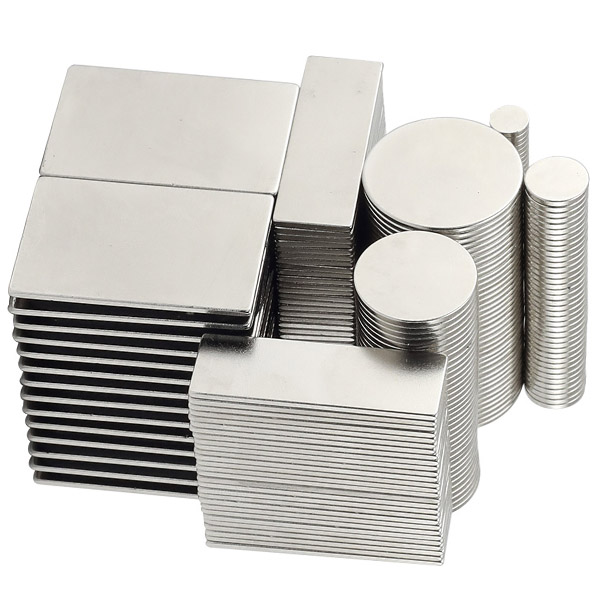
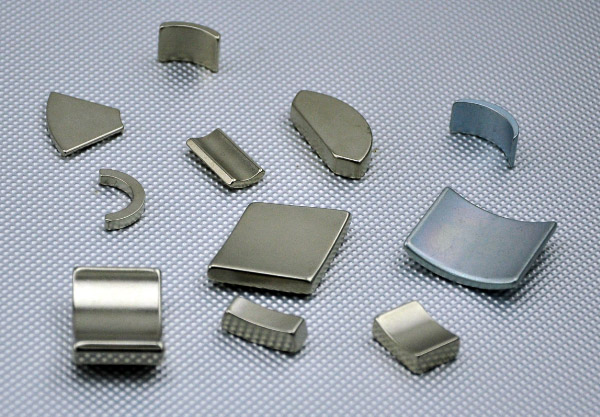
Item No.: ndfeb
Sintered Neodymium Magnet
Professional Neodymium Magnet manufacturer and exporter in China. NdFeB Magnet.
We are professional Neodymium Magnet manufacturer and exporter in China. We can produce Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet) according to your requirements. More types of Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet), Sintered Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet) wanted, please contact us right now.
General Introduction
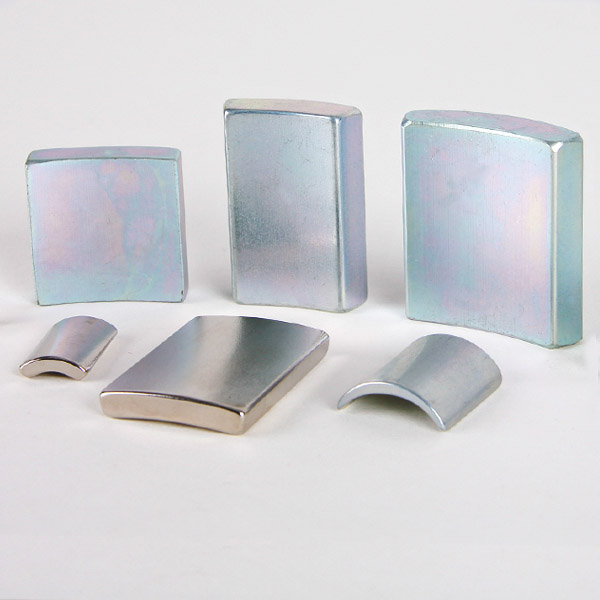
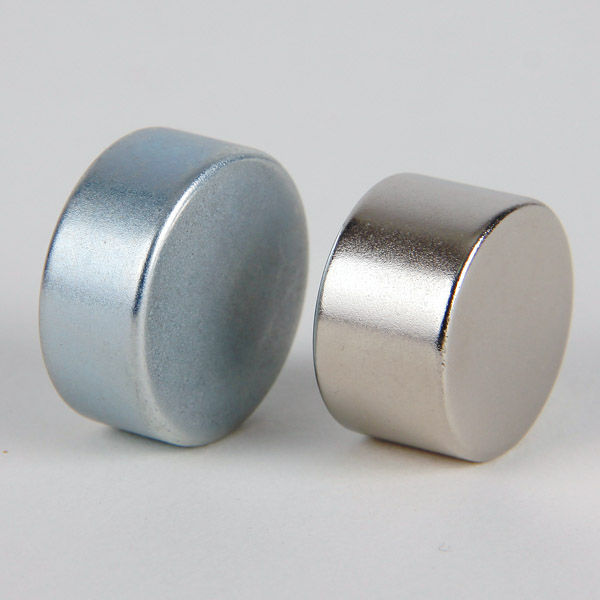
Sintered Neodymium Magnet is one of the high performance rare earth permanent magnets, which use neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), and boron (B) as their main ingredients and is susceptible to demagnetization when exposed to elevated temperatures. Neodymium magnet is a new kind of magnetic material developed with excellent magnetic characteristics. These magnets are extremely strong for their small size, metallic in appearance and found in simple shapes such as rings, blocks and discs. There are many grades which can stand high temperatures, but several factors will dictate the performance of the Neodymium magnet.
Neodymium Magnet can be used in sensors, motors, filter automobiles, magnetic holders, loudspeakers, wind generators, medical equipments etc.
Neodymium Magnets have the characteristics of :
* Super strong Br Resident induction. Excellent demagnetization resistance capability.
Good Price relative to its high magnetic properties.
Coating is needed for Neodymium Magnet
* Surface Treatment Method: Type Information
Metallic Zinc, Nickel, Nickel + Nickel, Copper + Nickel, Nickel + Copper + Nickel,
Gold, Organic Epoxy, Nickel + Epoxy coating
Temporary Surface: Passivation
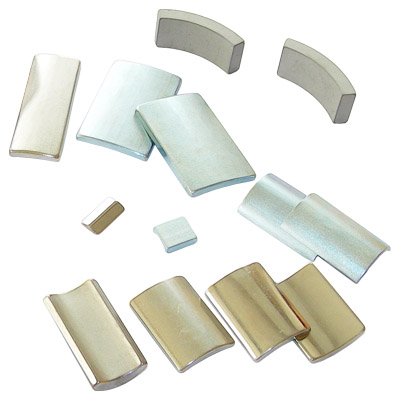
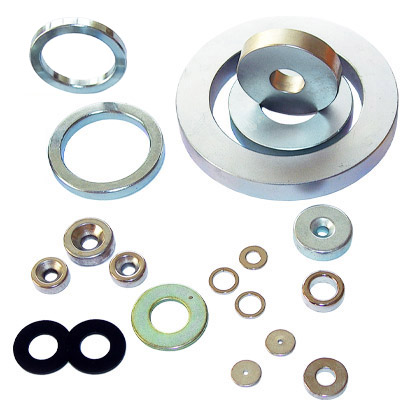
Dimension Available
Sintered Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet)s production process >>
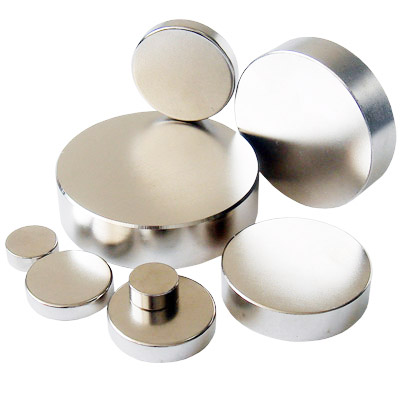
What shapes can it be formed? Neodymium Magnet
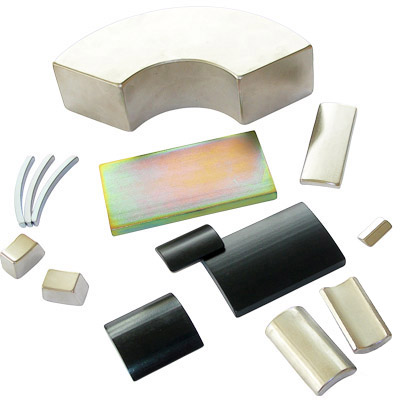 |  |
| Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet) for motor, generator, driver in various specification | Tile-shaped and special-shaped Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet) |
 |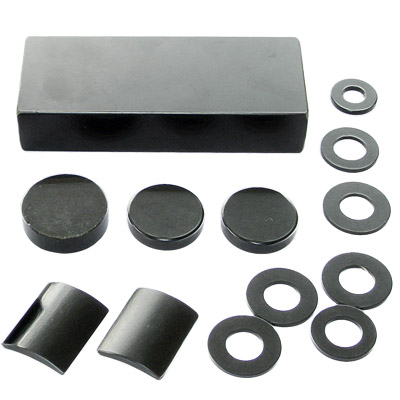  |
| Neodymium Magnet Blocks in various specification | Neodymium Magnet products painted with epoxy resin |
 |  |
| Neodymium Magnet Rings in various specification | Neodymium Magnet Cylinders in various specification |
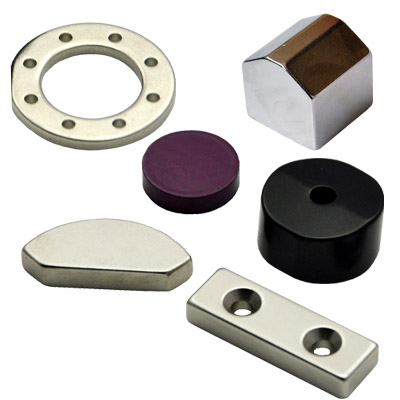 |  |
| Special Shape of Neodymium Magnet | Rubber Coated Neodymium Magnet |
 |  |
| Special Shape of Neodymium Magnet with 3M adhesive tape | QQMAG: Amazing Magnetic Sphere |
Magnetic properties of Sintered Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet):
| Grade | Remanence | Coercive Force | Intrinsic Coercive Force | Max. energy product | Max. Operating Temperature |
| Br mT (kGs) | Hcb kA/m (kOe) | Hcj kA/m (kOe) | ( BH )max kJ/m3 (MGOe) | Tw | |
| N35 | 1170-1220 | ≥ 868 | ≥ 955 | 263-287 | 80 ℃ |
| (11.7-12.2) | ( ≥ 10.9) | ( ≥ 12) | (33-36) | ||
| N38 | 1220-1250 | ≥ 899 | ≥ 955 | 287-310 | 80 ℃ |
| (12.2-12.5) | ( ≥ 11.3) | ( ≥ 12) | (36-39) | ||
| N40 | 1250-1280 | ≥ 907 | ≥ 955 | 302-326 | 80 ℃ |
| (12.5-12.8) | ( ≥ 11.4) | ( ≥ 12) | (38-41) | ||
| N42 | 1280-1320 | ≥ 915 | ≥ 955 | 318-342 | 80 ℃ |
| (12.8-13.2) | ( ≥ 11.5) | ( ≥ 12) | (40-43) | ||
| N45 | 1320-1380 | ≥ 923 | ≥ 955 | 342-366 | 80 ℃ |
| (13.2-13.8) | ( ≥ 11.6) | ( ≥ 12) | (43-46) | ||
| N48 | 1380-1420 | ≥ 923 | ≥ 876 | 366-390 | 80 ℃ |
| (13.8-14.2) | ( ≥ 11.6) | ( ≥ 12) | (46-49) | ||
| N50 | 1400-1450 | ≥ 796 | ≥ 876 | 382-406 | 60 ℃ |
| (14.0-14.5) | ( ≥ 10.0) | ( ≥ 11) | (48-51) | ||
| N52 | 1430-1480 | ≥ 796 | ≥ 876 | 398-422 | 60 ℃ |
| (14.3-14.8) | ( ≥ 10.0) | ( ≥ 11) | (50-53) | ||
| 30M | 1080-1130 | ≥ 796 | ≥ 1114 | 223-247 | 100 ℃ |
| (10.8-11.3) | ( ≥ 10.0) | ( ≥ 14) | (28-31) | ||
| 33M | 1130-1170 | ≥ 836 | ≥ 1114 | 247-263 | 100 ℃ |
| (11.3-11.7) | ( ≥ 10.5) | ( ≥ 14) | (31-33) | ||
| 35M | 1170-1220 | ≥ 868 | ≥ 1114 | 263-287 | 100 ℃ |
| (11.7-12.2) | ( ≥ 10.9) | ( ≥ 14) | (33-36) | ||
| 38M | 1220-1250 | ≥ 899 | ≥ 1114 | 287-310 | 100 ℃ |
| (12.2-12.5) | ( ≥ 11.3) | ( ≥ 14) | (36-39) | ||
| 40M | 1250-1280 | ≥ 923 | ≥ 1114 | 302-326 | 100 ℃ |
| (12.5-12.8) | ( ≥ 11.6) | ( ≥ 14) | (38-41) | ||
| 42M | 1280-1320 | ≥ 955 | ≥ 1114 | 318-342 | 100 ℃ |
| (12.8-13.2) | ( ≥ 12.0) | ( ≥ 14) | (40-43) | ||
| 45M | 1320-1380 | ≥ 995 | ≥ 1114 | 342-366 | 100 ℃ |
| (13.2-13.8) | ( ≥ 12.5) | ( ≥ 14) | (43-46) | ||
| 48M | 1360-1430 | ≥ 1027 | ≥ 1114 | 366-390 | 100 ℃ |
| (13.6-14.3) | ( ≥ 12.9) | ( ≥ 14) | (46-49) | ||
| 50M | 1400-1450 | ≥ 1033 | ≥ 1114 | 382-406 | 100 ℃ |
| (14.0-14.5) | ( ≥ 13.0) | ( ≥ 14) | (48-51) | ||
| 30H | 1080-1130 | ≥ 796 | ≥ 1353 | 223-247 | 120 ℃ |
| (10.8-11.3) | ( ≥ 10.0) | ( ≥ 17) | (28-31) | ||
| 33H | 1130-1170 | ≥ 836 | ≥ 1353 | 247-271 | 120 ℃ |
| (11.3-11.7) | ( ≥ 10.5) | ( ≥ 17) | (31-34) | ||
| 35H | 1170-1220 | ≥ 868 | ≥ 1353 | 263-287 | 120 ℃ |
| (11.7-12.2) | ( ≥ 10.9) | ( ≥ 17) | (33-36) | ||
| 38H | 1220-1250 | ≥ 899 | ≥ 1353 | 287-310 | 120 ℃ |
| (12.2-12.5) | ( ≥ 11.3) | ( ≥ 17) | (36-39) | ||
| 40H | 1250-1280 | ≥ 923 | ≥ 1353 | 302-326 | 120 ℃ |
| (12.5-12.8) | ( ≥ 11.6) | ( ≥ 17) | (38-41) | ||
| 42H | 1280-1320 | ≥ 955 | ≥ 1353 | 318-342 | 120 ℃ |
| (12.8-13.2) | ( ≥ 12.0) | ( ≥ 17) | (40-43) | ||
| 45H | 1300-1360 | ≥ 963 | ≥ 1353 | 326-358 | 120 ℃ |
| (13-13.6) | ( ≥ 12.1) | ( ≥ 17) | (43-46) | ||
| 48H | 1370-1430 | ≥ 995 | ≥ 1353 | 366-390 | 120 ℃ |
| (13.7-14.3) | ( ≥ 12.5) | ( ≥ 17) | (46-49) | ||
| 30SH | 1080-1130 | ≥ 804 | ≥ 1592 | 223-247 | 150 ℃ |
| (10.8-11.3) | ( ≥ 10.1) | ( ≥ 20) | (28-31) | ||
| 33SH | 1130-1170 | ≥ 844 | ≥ 1592 | 247-271 | 150 ℃ |
| (11.3-11.7) | ( ≥ 10.6) | ( ≥ 20) | (31-34) | ||
| 35SH | 1170-1220 | ≥ 876 | ≥ 1592 | 263-287 | 150 ℃ |
| (11.7-12.2) | ( ≥ 11.0) | ( ≥ 20) | (33-36) | ||
| 38SH | 1220-1250 | ≥ 907 | ≥ 1592 | 287-310 | 150 ℃ |
| (12.2-12.5) | ( ≥ 11.4) | ( ≥ 20) | (36-39) | ||
| 40SH | 1240-1280 | ≥ 939 | ≥ 1592 | 302-326 | 150 ℃ |
| (12.5-12.8) | ( ≥ 11.8) | ( ≥ 20) | (38-41) | ||
| 42SH | 1280-1320 | ≥ 987 | ≥ 1592 | 318-342 | 150 ℃ |
| (12.8-13.2) | ( ≥ 12.4) | ( ≥ 20) | (40-43) | ||
| 45SH | 1320-1380 | ≥ 1003 | ≥ 1592 | 342-366 | 150 ℃ |
| (13.2-13.8) | ( ≥ 12.6) | ( ≥ 20) | (43-46) | ||
| 28UH | 1020-1080 (10.2-10.8) | ≥ 764 | ≥ 1990 | 207-231 | 180 ℃ |
| ( ≥ 9.6) | ( ≥ 25) | (26-29) | |||
| 30UH | 1080-1130 (10.8-11.3) | ≥ 812 | ≥ 1990 | 223-247 | 180 ℃ |
| ( ≥ 10.2) | ( ≥ 25) | (28-31) | |||
| 33UH | 1130-1170 | ≥ 852 | ≥ 1990 | 247-271 | 180 ℃ |
| (11.3-11.7) | ( ≥ 10.7) | ( ≥ 25) | (31-34) | ||
| 35UH | 1180-1220 | ≥ 860 | ≥ 1990 | 263-287 | 180 ℃ |
| (11.8-12.2) | ( ≥ 10.8) | ( ≥ 25) | (33-36) | ||
| 38UH | 1220-1250 | ≥ 876 | ≥ 1990 | 287-310 | 180 ℃ |
| (12.2-12.5) | ( ≥ 11.0) | ( ≥ 25) | (36-39) | ||
| 40UH | 1240-1280 | ≥ 899 | ≥ 1990 | 302-326 | 180 ℃ |
| (12.5-12.8) | ( ≥ 11.3) | ( ≥ 25) | (38-41) | ||
| 28EH | 1040-1090 | ≥ 780 | ≥ 2388 | 207-231 | 200 ℃ |
| (10.4-10.9) | ( ≥ 9.8) | ( ≥ 30) | (26-29) | ||
| 30EH | 1080-1130 (10.8-11.3) | ≥ 812 | ≥ 2388 | 223-247 | 200 ℃ |
| ( ≥ 10.2) | ( ≥ 30) | (28-31) | |||
| 33EH | 1130-1170 | ≥ 836 | ≥ 2388 | 247-271 | 200 ℃ |
| (11.3-11.7) | ( ≥ 10.5) | ( ≥ 30) | (31-34) | ||
| 35EH | 1170-1220 | ≥ 876 | ≥ 2388 | 263-287 | 200 ℃ |
| (11.7-12.2) | ( ≥ 11.0) | ( ≥ 30) | (33-36) | ||
| 38EH | 1220-1250 | ≥ 899 | ≥ 2388 | 287-310 | 200 ℃ |
| (12.2-12.5) | ( ≥ 11.3) | ( ≥ 30) | (36-39) | ||
| 30AH | 1080-1120 | ≥ 812 | ≥ 2785 | 223-255 | 220 ℃ |
| (10.8-11.2) | ( ≥ 10.2) | ( ≥ 35) | (28-32) | ||
| 33AH | 1120-1170 | ≥ 812 | ≥ 2785 | 247-271 | 220 ℃ |
| (11.2-11.7) | ( ≥ 10.2) | ( ≥ 35) | (31-34) |
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Neodymium Magnet:
| Thermal Conductivity | 7.7 kcal/m-h-°C |
| Young’s Modulus | 1.7 x 104 kg/mm² |
| Bending Strength | 24 kg/mm² |
| Compressive Strength | 80 kg/mm² |
| Electrical Resistivity | 160 µ-ohm-cm/cm² |
| Density | 7.4-7.55 g/cm³ |
| Vickers Hardness | 500 - 600 |
Available coatings for sintered Neodymium Magnet (NdFeB magnet):
| Available Coatings: | ||||
| Surface | Coating | Thickness (Microns) | Color | Resistance |
| Passivation | 1 | Silver Grey | Temporary Protection | |
| Nickel | Ni+Ni | 10-20 | Bright Silver | Excellent against Humidity |
| Ni+Cu+Ni | ||||
| Zinc | Zn | 8-20 | Bright Blue | Good Against Salt Spray |
| C-Zn | Shinny Color | Excellent Against Salt Spray | ||
| Tin | Ni+Cu+Sn | 15-20 | Silver | Superior Against Humidity |
| Gold | Ni+Cu+Au | 10-20 | Gold | Superior Against Humidity |
| Copper | Ni+Cu | 10-20 | Gold | Temporary Protection |
| Epoxy | Epoxy | 15-25 | Black, Red, Grey | Excellent Against Humidity & Salt Spray |
| Ni+Cu+Epoxy | ||||
| Zn+Epoxy | ||||
| Chemical | Ni | 10-20 | Silver Grey | Excellent Against Humidity |
| Parylene | Parylene | 5-20 | Grey | Excellent Against Humidity, Salt Spray. Superior Against Solvents, Gases, Fungi and Bacteria. FDA Approved. |
Magnetisation Direction of Magnet
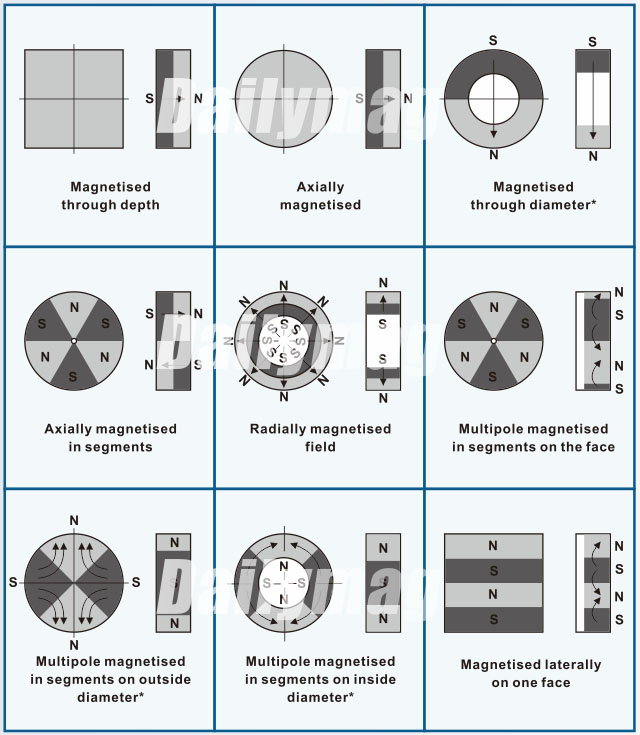
1. Magnetised through depth
2. Axially magnetised
3. Magnetised through diameter*
4. Axially magnetised in segments
5. Radially magnetised
6. Multipole magnetised in segments on the face
7. Multipole magnetised in segments on outside diamater*
8. Multipole magnetised in segments on inside diamater*
9. Magnetised laterally on the face
All available for magnet is isotropic or anisotropic except*
Production Flow of Neodymium Magnet:
| 1. Raw Material | 2. Melting | 3. Milling |
| 4. Pressing | 5. Vacuum Sintering | 6. Machining |
| 7. Coating | 8. Magnetization | 9. Final Inspection |
Application of Neodymium Magnet:
1. Computers: VCM, Printers
2. Machinery: Magnetic separtors, Robots
3. Transportation: Levitation train, Electric vehicle
4. Medical Service: MRI, Magnetic-therapy devices
5. Energy: Genertator, Electric motor
6. Communication: Mobile telephone, Voice and data, Communication system
7. Electical Appliance: HiFi system, Air conditioner
8. Oil Chemical Industry: Magnetic vibrating device for reducing viscosity and condensation, Nuclear magnetic logging tools, Anti-waxer of oil wells
More useful information of Dailymag Neodymium magnets:
Neodymium magnets are crystalline structures made of iron, boron, and neodymium alloy. These are the permanent magnets with extremely efficient magnetic abilities due to which they are abundantly being used. These strongest magnets were first made in 1984, and now are available commercially at a large scale because of their applications in different types of machinery I.e., hard disks, electric motors, magnetic fasteners, and cordless tools, etc. Neodymium magnets have become a preferred choice among the different magnets available in the market, due to high quality of magnets used at a very affordable cost. Our high-quality, extremely reliable, and durable neodymium magnets are available in a very affordable range.
Available neodymium magnets:
You can get licensed neodymium magnets at a wide range in different forms as per your requirements. Our neodymium variety includes rectangular, plane disc, curved discs square, circular, rings, beads, balls, cylinder, arc, trapezoid, and block shaped magnets. Moreover, we also facilitate our customers by providing them with custom-sized neodymium magnets according to their given specifications and requirements. We can also provide our duties for the customers who want neodymium magnets in any shape other than the mentioned ones and any size because of our experienced staff and advanced manufacturing resources.
General properties:
Our neodymium magnets meet the standard requirements and contain the following features:
- These magnets have proven to be strongest of all the Rare-Earth magnets available.
- These are made of three components: Iron (Fe), Neodymium (Nd), and Boron (B).
- Their extent of saturation magnetization is very high.
- Neodymium magnets can resist demagnetization due to their saturation magnetization.
- A smaller neodymium magnet can replace a larger ordinary magnet because of its higher magnetic strength.
- Neodymium magnets are more durable as these can last for more than 10 years because of very little change in their flux density.
- The flux density and magnetization ability of neodymium magnets are influenced by charged fields and high temperature.
- Resistant to crack or chip of without any intentional and extremely hard external force.
- Neodymium magnets are less costly and are affordable.
- We have a wide range of grades available in neodymium magnets i.e., N30 (M, H, SH), N35, N38, to N50 (M, H,).
- (The grades of magnets are sets depending upon their maximum energy product which is also related to their magnetic flux. The high-grade value indicates a strong magnetic tendency of the magnets).
- Our neodymium magnets are available in different shapes as per requirement I.e., rings, discs, cylinders, balls, beads, blocks, slits etc.
- We manufacture our neodymium magnets to ensure high reminisce (strength of magnetic field).
- Neodymium magnets are highly coercive or resistant towards demagnetization.
- They also have high maximum energy products.
- Neodymium magnets have low Curie temperature.
- Neodymium magnets are vulnerable to corrosion along their boundaries. Therefore, we ensure Nickel or Copper-based outer coverings to prevent corrosion.
- Their resistance toward demagnetization reduces with an increase in temperature. However in the room that have high coactivity.
- These magnets are not made to be used at sites with a temperature greater than 130° C.
- At working place, we use super glues to carry the assembly of these magnets.
Dailymag try our best to ensure the best quality of our magnets, however, the conditions of the customer's project may demand a certain type of material. Therefore, we highly appreciate our customers discussing their applications which may help them in selecting the best suitable material for them.
Factors affecting the magnetic strength:
Neodymium is a ferromagnetic metal that shows high magnetism in very low temperatures because its Curie temperature is -254.2 and above this temperature, its ferromagnetic abilities start to reduce. In magnets, neodymium is therefore combined with transition metals, which results in a Curie temperature relatively more than the normal room temperature, and enables the magnet to retain its ferromagnetic properties.
Factors that play part in the strengthening of the magnets are as follows:
- The tetragonal crystalline nature of the Nd2Fe14B magnet makes it have more tendency to be magnetized more in one direction as compared to the others.
- Microstructure: while manufacturing, we make our magnets with microcrystalline grains, arranged to keep their direction of magnetization in one axis due to which it becomes difficult to change the magnetic direction.
- Saturation magnetization: neodymium has four free electrons as compared to iron (three free electrons) which increases the saturation magnetization of neodymium magnet.
- Magnetic energy: the magnetic energy of our neodymium magnets is almost 18 times more than the normally used ordinary iron magnets in terms of volume. Our neodymium magnets have more magnetic energy than other rare earth metals as well i.e., samarium cobalt magnets.
- Alloy composition: The magnetic property of our neodymium magnets also depends upon their relative alloy composition. Boron does not play any major role in magnetism but is added to enhance and strengthen the covalent bonding.
Applications:
Neodymium magnets are the most widely demanded permanent magnets, nowadays, that have managed to replace ferric and alnico magnets because of advanced and more reliable characteristics. Neodymium magnets are used within modern technology as components because they take less space and provide more magnetic strength. These magnets are used in locks, computer hard disks, loudspeakers, mechanical switches, electric motors, wind turbine generators, spectrometers, power steering, compressor motors, voice coils, and many other technologies. Recently, neodymium magnets have also being used in making children's toys i.e., building sets, jewelry clasps, desk-toy magnets such as Buckyballs, etc. Neodymium magnets have wide range of applications and till date being used in medical technology such as magnetic resonance imaging scanners and the radiology department. They are also used in a surgically placed anti-reflux system that comprises the placement of a magnet band inside the body.
Precautions:
While dealing with neodymium magnets some precautions are very necessary. These magnets are very hard and brittle. In case of any crack, it may pose injury. They contain high magnetic strength and are held with certain care. Sometimes you will see some of the magnet chipping off and this can cause damage to the surrounding or injuries to handlers. Neodymium magnets must be handled at room temperature or near room temperatures. Otherwise, it can behave opposite to the expectation.